Exploring Russian Tortoise Reproduction: Discover Their Intriguing Behaviors!
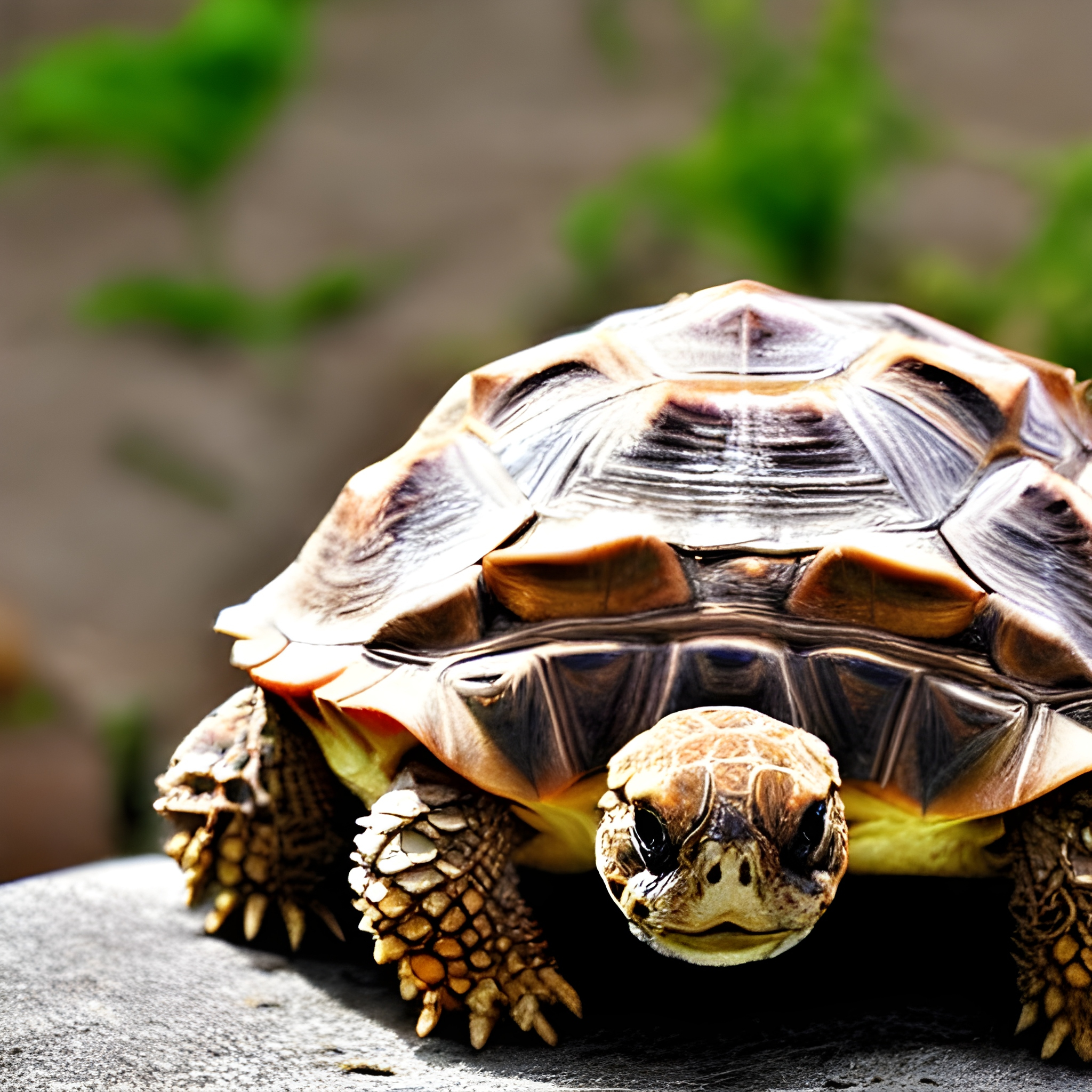

Introduction:
Step into the enchanting world of Russian tortoise reproduction and discover the captivating behaviors that make these creatures truly remarkable. From intricate courtship rituals to perfectly timed mating seasons, these tortoises demonstrate a fascinating array of reproductive strategies that have captured the curiosity of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
In this article, we delve into the secrets of Russian tortoise reproduction, shedding light on their unique behaviors and shedding new light on their extraordinary adaptation strategies. Join us as we uncover the incredible ways in which these tortoises navigate the challenges of reproduction, from nesting behaviors to intriguing mating rituals.
Whether you’re a tortoise enthusiast looking to expand your knowledge or simply intrigued by the wonders of the natural world, this article is sure to captivate your imagination. So, embark on this journey with us as we unveil the hidden wonders of Russian tortoise reproduction and gain a deeper understanding of their extraordinary behaviors.
Experience the adventure and explore the intricacies of Russian tortoise reproduction today!
Understanding the reproductive behavior of Russian tortoises:
Russian tortoises (Agrionemys horsfieldii) have a complex reproductive behavior that is influenced by various factors. These small tortoises, native to Central Asia, are known for their unique adaptations and survival strategies. Understanding their reproductive behavior is key to appreciating their remarkable evolutionary journey.
One of the key factors that influence Russian tortoise reproduction is their response to environmental cues. These tortoises have developed a keen sense of timing, relying on temperature and light patterns to determine the onset of the breeding season. As the temperatures rise and the days get longer, male tortoises become more active and display courtship behaviors to attract females.
Mating rituals and courtship behaviors:
During the breeding season, male Russian tortoises engage in elaborate courtship rituals to attract females. These rituals involve head bobbing, circling, and even gentle biting. The purpose of these behaviors is to establish dominance and gain the attention of potential mates.
Once a male has successfully courted a female, mating takes place. The male mounts the female from behind and uses his hind legs to secure his position. This process can last for several hours and is a crucial step in the reproductive cycle of Russian tortoises.
Nesting habits and egg laying process:
After successful mating, female Russian tortoises begin searching for suitable nesting sites. These tortoises have a strong instinct to find areas with loose soil or sandy substrate, which allows them to dig burrows for egg deposition. The depth and size of the burrow depend on the size of the female tortoise and the number of eggs she carries.
Once the burrow is prepared, the female tortoise lays her eggs one by one, carefully placing them in the nest. The number of eggs laid varies, with larger females laying more eggs than smaller ones. After the eggs are laid, the female covers the nest with soil, effectively hiding it from potential predators.
Incubation period and hatching of Russian tortoise eggs:
The incubation period of Russian tortoise eggs typically lasts between 70 to 90 days, depending on environmental conditions. The temperature plays a crucial role in determining the sex of the hatchlings, with higher temperatures resulting in more females and lower temperatures favoring the development of males.
During the incubation period, the eggs are left unattended, and the mother tortoise focuses on conserving energy. The eggs absorb moisture from the surrounding soil, providing the necessary hydration for the developing embryos. As the incubation period nears its end, the embryos start to develop, and the eggs become more opaque.
Parental care and protection of hatchlings:
Once the hatchlings emerge from their eggs, they are entirely independent and must navigate the world on their own. The mother tortoise does not provide any parental care or protection to the hatchlings, as they are born with the necessary instincts to survive.
The hatchlings are equipped with a hard shell and strong claws, allowing them to defend themselves against potential threats. They rely on their instincts to find food and shelter, and their small size helps them evade predators. However, the mortality rate of Russian tortoise hatchlings is relatively high, with only a small percentage surviving to adulthood.
Factors affecting reproductive success in Russian tortoises:
Several factors can influence the reproductive success of Russian tortoises. Habitat loss and fragmentation due to human activities pose a significant threat to tortoise populations. Destruction of nesting sites, pollution, and climate change can disrupt the delicate balance necessary for successful reproduction.
In addition to external factors, the age and health of the tortoises also play a crucial role in their reproductive success. Older and healthier individuals tend to have higher fertility rates and produce more viable offspring. Maintaining a healthy environment and providing proper care for captive tortoises can help increase their chances of successful reproduction.
Conservation efforts for Russian tortoise populations:
Due to the declining population of Russian tortoises in the wild, conservation efforts have become crucial for their survival. Captive breeding programs, habitat restoration, and public awareness campaigns are being implemented to protect these fascinating creatures and their unique reproductive behaviors.
Captive breeding programs aim to breed Russian tortoises in controlled environments and release them back into the wild to boost population numbers. These programs also provide valuable insights into the reproductive biology of these tortoises, helping scientists develop effective conservation strategies.
Tips for breeding Russian tortoises in captivity:
If you’re a tortoise enthusiast interested in breeding Russian tortoises in captivity, there are several considerations to keep in mind. Providing a suitable habitat with ample space, proper temperature gradients, and UVB lighting is essential for the health and well-being of the tortoises.
Creating a stimulating environment that mimics their natural habitat encourages natural behaviors, including courtship and mating. It’s also important to ensure a balanced diet, including a variety of leafy greens, vegetables, and occasional fruits. Regular veterinary check-ups and monitoring of reproductive behaviors can help identify any issues and ensure successful breeding.
Conclusion: Appreciating the wonder of Russian tortoise reproduction
Russian tortoises have captivated the world with their unique reproductive behaviors and remarkable adaptation strategies. From intricate courtship rituals to perfectly timed nesting behaviors, these tortoises navigate the challenges of reproduction with astonishing precision.
By understanding their reproductive behavior, we gain a deeper appreciation for the wonders of the natural world and the intricate web of life. As we continue to explore and protect the habitats of Russian tortoises, we ensure the survival of these fascinating creatures and their extraordinary reproductive behaviors.
Embark on this journey of discovery, and let the world of Russian tortoise reproduction unfold before your eyes. Experience the wonder, embrace the marvel, and gain a newfound respect for the captivating behaviors of these remarkable creatures.





One Comment